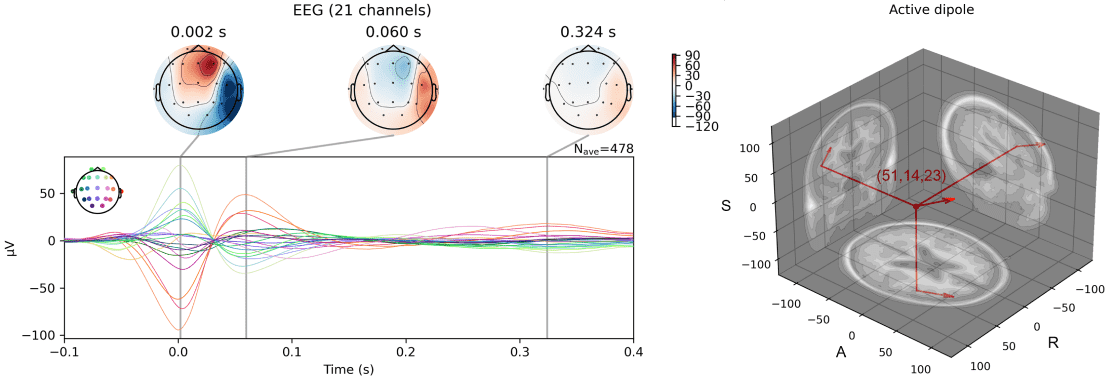
EEG source localization is a non-invasive method that uses scalp-recorded potential signals to inversely calculate the location, direction, and intensity of intracranial neural activity sources. In clinical research, EEG source localization has become an important tool for preoperative assessment of drug-resistant epilepsy patients due to its non-invasive nature and ease of operation, and has proven its value in guiding epileptogenic zone localization and SEEG implantation planning in multiple studies. In practice, it commonly analyzes interictal spike discharge events identified through non-invasive methods such as electroencephalography (EEG) and magnetoencephalography (MEG) to provide estimates of the irritative zone. This technology also plays a key role in localizing high-frequency oscillations, motor imagery, working memory, and other brain functional area activity studies.